What Does Diabetes Do to Your Teeth?
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how your body processes glucose that is sugar. Nearly 11.4% of India’s population is living with diabetes. While most people are aware of the impact of diabetes on various organs, one aspect that often goes unnoticed is its effect on oral health. In this detailed article, we will examine the effects of diabetes on your teeth. Understanding this connection is crucial for individuals living with diabetes, as it can help them take proactive steps to maintain good oral health.
The Diabetes-Oral Health Connection
1. Increased Risk of Gum Disease
One of the primary ways diabetes affects your teeth is by increasing the risk of gum disease. Periodontal disease, commonly referred to as gum disease, can progress more rapidly and severely in individuals with diabetes.
- Blood Sugar Levels: High blood sugar levels in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes can create an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive in the mouth which leads to gum inflammation and infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Diabetes can weaken the body’s ability to fight off infections, making it harder to combat gum disease.
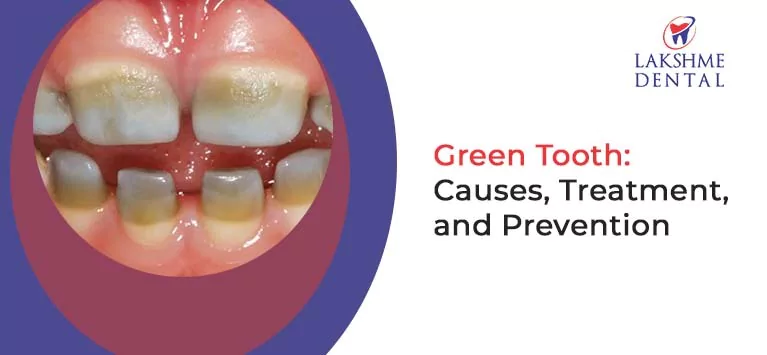
2. Tooth Decay
Diabetes can also contribute to tooth decay, though the connection is not as direct as with gum disease.
- Dry Mouth: People with diabetes are more prone to having a dry mouth, which means reduced saliva production. Saliva prevents tooth decay by washing away food particles.
3. Your wounds Take Longer to Heal:
- Poor Healing: Slower wound healing in people with diabetes can affect the recovery from dental procedures like fillings and extractions, potentially leading to complications.
4. Bad Breath
Bad breath, or halitosis, can be associated with diabetes due to factors like dry mouth and increased bacterial activity. In diabetes, reduced saliva flow creates an environment where bacteria thrive, contributing to unpleasant breath.
5. Yeast Infection:
Sugar isn’t just a treat for bacteria but it’s also a favorite for fungi. In diabetes, the likelihood of developing a fungal yeast infection like oral thrush increases. Oral thrush can manifest as white or red patches on the tongue and inside the cheeks, potentially progressing to open sores.
Factors like wearing dentures, smoking, or taking antibiotics can heighten the risk, as the yeast thrives on the extra sugar in saliva, especially in moist areas like those beneath loose-fitting dentures.
6. Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning Mouth Syndrome, a condition causing a burning sensation in the mouth, can be linked to diabetes, affecting oral health. Individuals with diabetes may experience this discomfort, and experience a tingling sensation.
Managing Diabetes and Oral Health
Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
The first and most crucial step in protecting your oral health when you have diabetes is to control your blood sugar levels effectively.
- Monitor Regularly: Monitor your blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Medications and Insulin: Take prescribed medications or insulin on schedule.
- Diet and Exercise: Follow a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to help manage blood sugar.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential to detect and address oral health issues early. These visits can help manage and prevent complications related to diabetes.
- Schedule Routine Visits: Visit your dentist at least every six months for routine check-ups.
- Communication: Inform your dentist about your diabetes and any changes in your condition.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent gum disease and tooth decay.
- Brush and Floss: Brush your teeth at least once a day and floss daily to remove plaque and other food particles.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Choose a fluoride toothpaste to strengthen tooth enamel.
- Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to help control bacterial growth.
Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet is beneficial for both diabetes management and oral health.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce your consumption of sugary and starchy foods that can contribute to tooth decay.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into your diet for essential nutrients.
Hydration
Maintaining adequate hydration can help alleviate dry mouth.
- Drink Water: Stay well-hydrated by drinking a lot of water throughout the day.
Smoking Cessation
For individuals with diabetes who smoke, quitting smoking is vital for oral health.
- Seek Support: Consider seeking support or resources to help you quit smoking.
Key Takeaway
In conclusion, diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth decay, but with proactive steps, these risks can be minimized.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, controlling blood sugar levels, and seeking regular dental care are essential for individuals living with diabetes.
By following these guidelines and working closely with healthcare providers, it is possible to preserve oral health and prevent complications related to diabetes. If you are looking for dental advice or treatment, you can visit Lakshme Dental in Tirunelveli for a consultation. Always keep in mind that oral health is an integral part of your overall well-being, and it is within your control to protect your smile, even when managing diabetes.